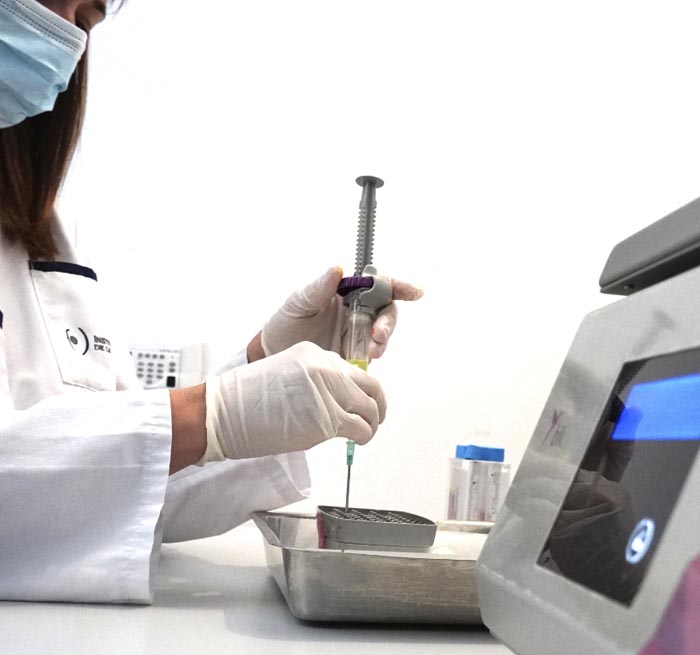
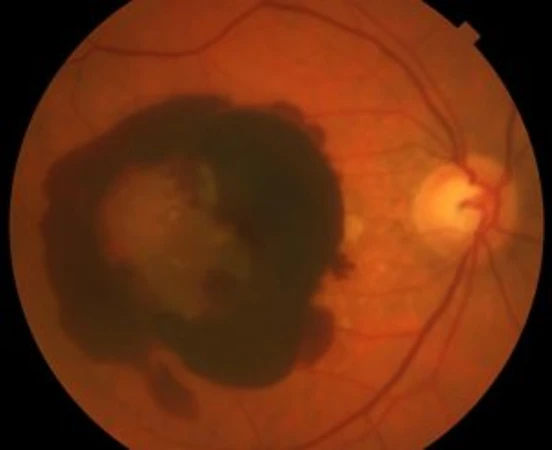
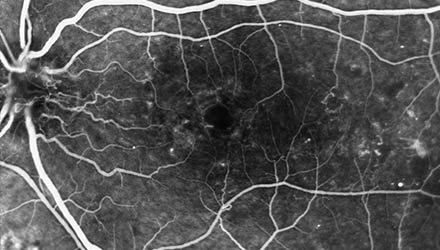
Intraocular hemorrhage or ocular hemorrhage, also called vitreous hemorrhage, is bleeding inside the vitreous cavity. This is the internal area of the eye.
The vitreous is a gelatinous and transparent substance that occupies two-thirds of the ocular volume. It is composed of 99% water. It borders posteriorly with the retina and anteriorly with the lens and the ciliary body.
The most frequent cause of intraocular hemorrhage is diabetic retinopathy, responsible for 50% of cases. Other common causes are rhegmatogenous retinal detachment and posterior vitreous detachment.
It can also be caused by obstruction of the central retinal vein. These conditions are responsible for 95% of cases of spontaneous vitreous hemorrhage.