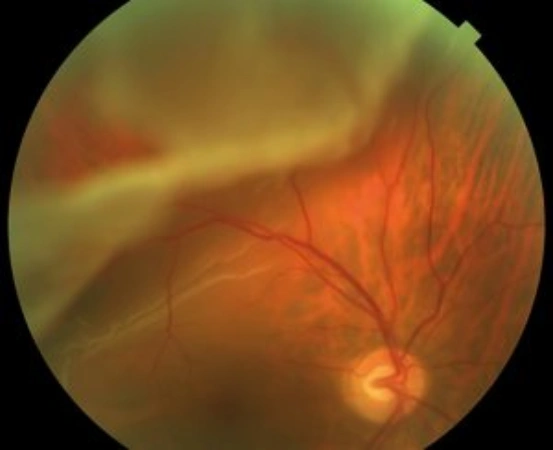
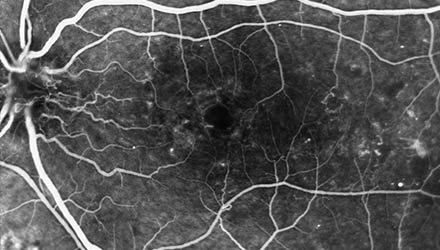
Retinal detachment has an incidence of approximately one in every 15,000 people. This event, which can occur at any age, is more frequent in myopic patients or those with a history of the disease.
The retina is a thin layer that covers the inner part of the posterior wall of the eye, where the images that are sent to the brain are focused. Under normal conditions, the retina is attached to a more external layer, the retinal pigment epithelium. Conceptually, retinal detachment refers to the separation between the layers of the neurosensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium.