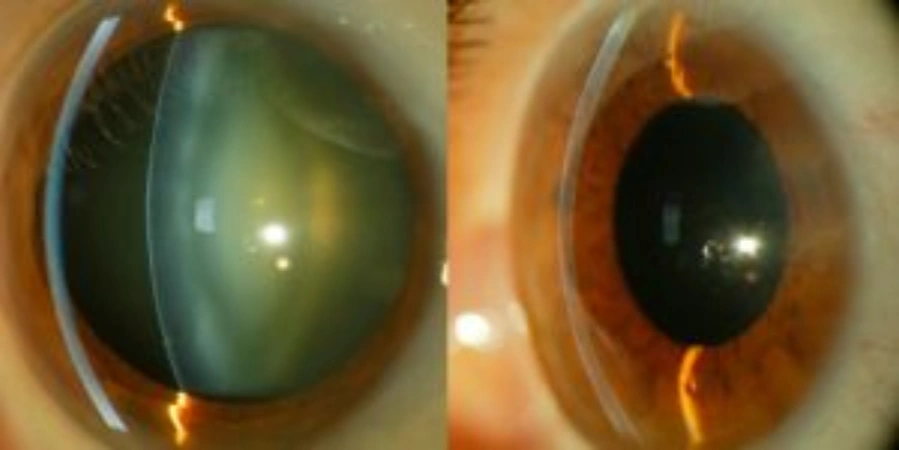
Ocular cataract is one of the most common ocular disorders. It is defined as any opacity of the lens, a fundamental part of the ocular system. The lens focuses the light rays that enter the eye onto the retina and, over the years, it gradually loses transparency. Although ocular cataract tends to progress slowly, it is common for both eyes to eventually be affected, causing glare and a partial or complete loss of images. Cataract surgery may be necessary when vision is significantly affected.
Ocular cataract is a pathology of multifactorial origin, with age as the main risk factor. Various diseases, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity, as well as other external factors such as smoking, malnutrition, and ionizing radiation, can contribute to the development of ocular cataracts.
In addition to senile cataract, other types of ocular cataracts may develop, such as congenital or infantile cataracts, those secondary to trauma, associated with metabolic disorders, or caused as a side effect of certain medications, such as corticosteroids.
Cataract surgery is the most common treatment to restore vision in advanced cases. This procedure is usually performed using minimally invasive techniques with a fast recovery. If you have severe ocular cataracts, cataract surgery may be the solution to improve your quality of life and vision.