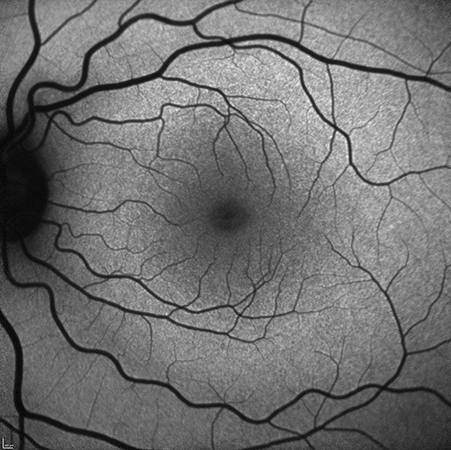
Fundus autofluorescence imaging is a non-invasive technique that provides detailed information about the onset and progression of disease.
The autofluorescence technique utilizes the fluorescent properties of a metabolic indicator called lipofuscin to study the health and viability of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) complex. While other fluorochromes can be detected in the outer retina in disease conditions, lipofuscin is the primary source of intrinsic fluorescence in the fundus. Excessive accumulation of lipofuscin granules within the lysosomal compartment of RPE cells represents a common pathogenic pathway for various complex and hereditary retinal diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD).