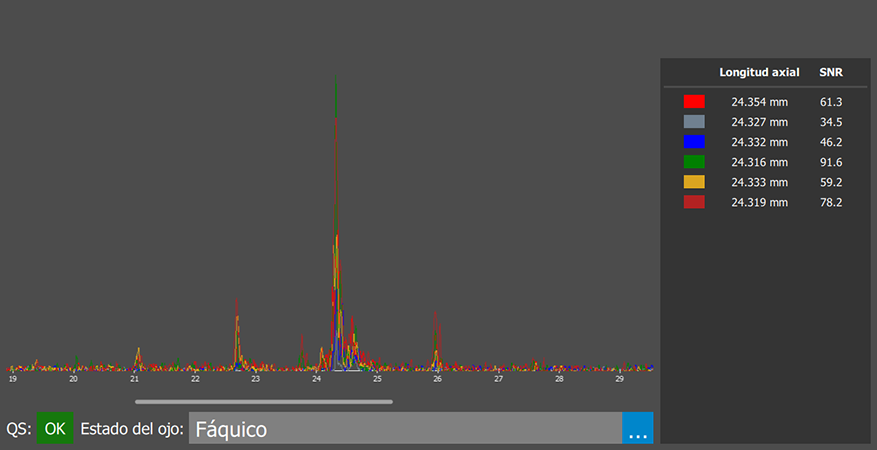
Axial length is the distance from the corneal vertex, on the epithelial side, to the retinal foveola along the visual axis. It is essential to determine this measurement whenever an intraocular lens is calculated after removing an optical element from the eye.
A refractive error in axial length measurement can have a significant impact, especially since the goal of lens surgery is often to achieve emmetropia.
Axial length is measured using ocular biometry. This is done with an optical biometer called the IOL Master.
Using a non-contact technique, the IOL Master measures the anteroposterior axis through a method known as partial coherence interferometry, which aligns with the visual axis.
For biometry, the patient is typically positioned in front of a high-precision device, which emits a laser signal to capture images.
Generally, no special preparation is required for this exam.