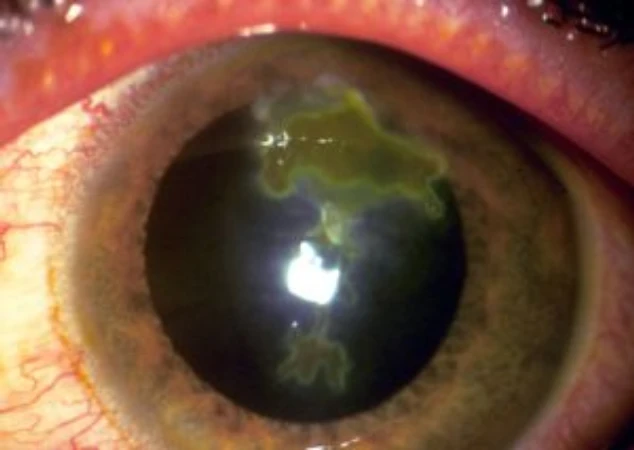
The herpes virus family is an important cause of eye infection, known as ocular herpes. Infection by the virus affects almost all ocular tissues, such as the eyelid, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, trabecular meshwork, and retina.
The most frequent manifestations of an ocular infection by the ocular herpes virus are:
- Blepharoconjunctivitis: involvement of the eyelid and conjunctiva, often combined with palpable preauricular lymph nodes. Vesicles appear on the skin or eyelid margin.
- Epithelial keratitis: causes foreign body sensation, photophobia, redness, and blurred vision.
- Stromal keratitis: occurs when the infection affects the deeper layers of the cornea, causing stromal edema, with decreased vision, photophobia, and pain.
- Iridocyclitis: inflammation of the anterior chamber of the eye, associated with elevated intraocular pressure, causing light sensitivity, blurred vision, pain, and eye redness.