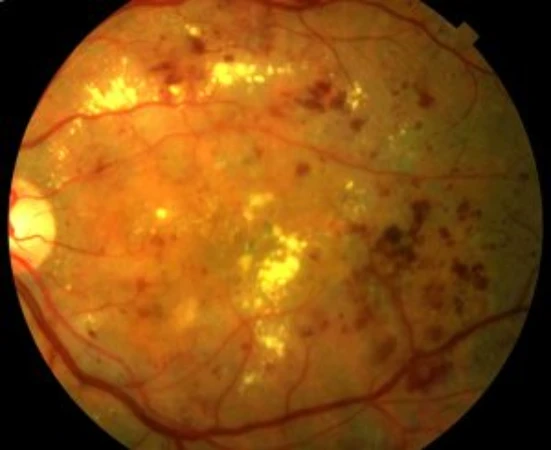
Diabetic retinopathy is currently the most common cause of vision loss of vascular origin. It is characterized by the deterioration of the blood vessels in the retina, which can manifest as fluid leakage and the appearance of diabetic macular edema and, in more severe cases, complete occlusion of the vessels, leading to severe retinal ischemia. In an attempt to improve circulation, new low-quality blood vessels (neovessels) are produced, which are responsible for the complications associated with what is known as proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
When a diabetic patient also presents other risk factors such as high blood pressure, obesity, high cholesterol, or smoking, the risk of developing ocular complications multiplies. For this reason, a patient suffering from diabetic retinopathy must be very disciplined in managing their overall health, diet, and weight control, and must avoid smoking. Even if no symptoms are present, the patient must undergo regular ophthalmological check-ups. Prevention and early diagnosis drastically improve the visual prognosis of the disease. Nowadays, in most patients, it is possible to avoid reaching extreme situations such as blindness.
In few diseases is the benefit of prevention so high.
Pregunta-li a ChatGPT