How refractive errors are corrected
Refractive surgery aims to reduce or eliminate patients’ dependence on optical correction (glasses or contact lenses) permanently.
Currently, we have a set of surgical techniques that correct refractive errors permanently and allow us to avoid dependence on glasses. Among these refractive surgery techniques, we distinguish two types:
Laser techniques, which are performed on the cornea. They are the most used in cases of myopia, hyperopia, and low to moderate astigmatism.
Phakic intraocular lens techniques. These are usually employed in cases of higher prescriptions or when, for some reason, a laser technique cannot be applied. The current trend, given the safety, predictability, and quality of vision they provide to patients, is to use intraocular lens techniques for smaller and smaller refractive errors.
Refractive surgery techniques
Corneal refractive surgery
LASIK
The most commonly used laser refractive surgery is LASIK. It consists of modifying the shape of the cornea to change the refraction or total prescription of the eye. To do this, the first layers of corneal tissue (corneal flap) are carefully separated, either mechanically or with the femtosecond laser, and then the excimer laser is applied, which reshapes the cornea to correct the desired diopters. Finally, the treated area is covered again with the corneal flap, without stitches, to restore the normal ocular surface.
The excimer laser we use at the Institut de la Màcula allows us to perform customized treatments to increase precision in correction and improve visual quality, while also preserving corneal thickness more efficiently.
LASIK refractive surgery is performed with topical anesthesia, lasts only a few minutes, is painless, and visual recovery is practically immediate. Within a few hours, the patient can perform most daily activities without the need for glasses.
PRK
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) with excimer laser is a surgical technique through which diopters are corrected with superficial corneal ablation. With this technique, the laser is applied directly to the external surface of the cornea to sculpt a new optical surface beneath the epithelium.
The main advantages of PRK are its simplicity, safety (no corneal flap required), and precision. However, at the end of the treatment, it leaves a corneal area denuded of the epithelium, which must regenerate. This causes postoperative discomfort during the first few days.
PRK is preferable in some cases, especially to correct low myopia and in cases of superficial corneal opacities that one wishes to remove.
Refractive surgery with phakic lens implant
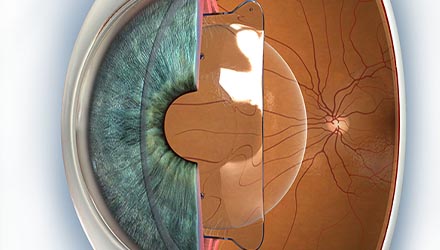
ICL lens implant
The phakic ICL lenses are those we use at the Institut de la Màcula. They are implanted between the iris and the crystalline lens without removing it. The main advantage of these lenses is that they are a reversible procedure with which, if the intraocular spaces allow, we can correct very severe hyperopia and myopia.
Some considerations
The choice of the most appropriate refractive surgery technique for each person depends on several factors. It is essential that the refractive error remains stable for at least one year and that the patient is over eighteen years old and highly motivated to undergo the procedure.
The surgeon takes into account the number of diopters to be corrected, the corneal characteristics in terms of shape, curvature, regularity, and thickness, the characteristics of the anterior segment of the eye and the depth of the anterior chamber, and also evaluates, after completing a full ophthalmological examination, the condition of the different ocular structures.
Specific complementary tests are carried out and, once these factors have been carefully assessed, the specialist advises on the most appropriate and safest refractive surgery technique for each particular case.
Complementary tests
Pentacam AXL WAVE