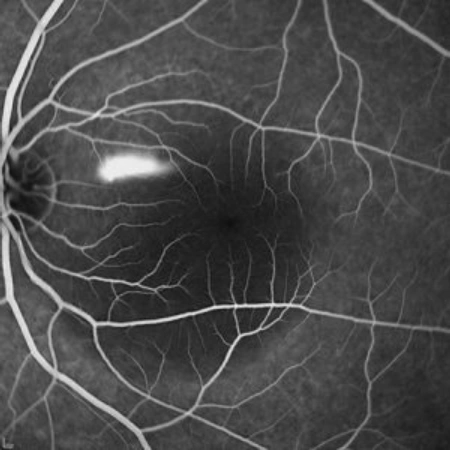
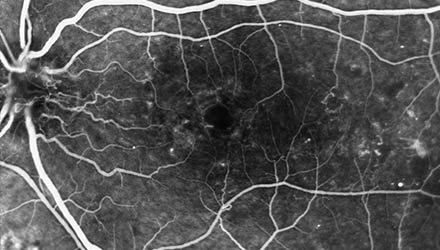
Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) is a relatively common ocular condition. It affects both healthy young and adult individuals.
It is characterized by a focal alteration in the permeability of the retinal pigment epithelium. This alteration causes fluid leakage from the choroid. The choroid is the layer of blood vessels beneath the retina. The fluid moves toward the subretinal space. This causes a detachment of the neurosensory retina. Usually, but not always, it affects the macular and foveal region. The detachment prevents the photoreceptors from being properly nourished. This causes them to stop functioning correctly.
Several risk factors have been associated with the onset of central serous chorioretinopathy. Some of these factors include the administration of certain medications, especially corticosteroids by any route, or stressful situations.